According to James Webb Space Telescope official documentation (cfr. https://jwst-docs.stsci.edu/jwst-mid-infrared-instrument) the JWST Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) provides imaging and spectroscopic observing modes from 4.9 to 27.9 μm. These wavelengths can be utilized for studies including, but not limited to: direct imaging of young warm exoplanets and spectroscopy of their atmospheres; identification and characterization of the first galaxies at redshifts z > 7; and analysis of warm dust and molecular gas in young stars and proto-planetary disks.
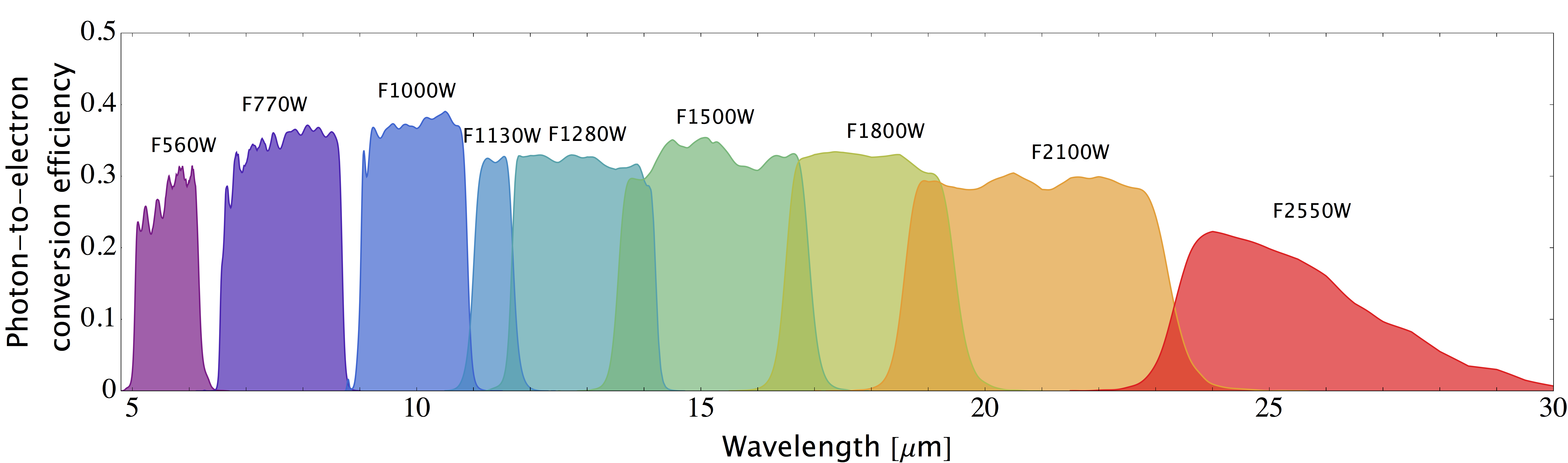
MIRI imaging filter curves and wavelenght are resumed below

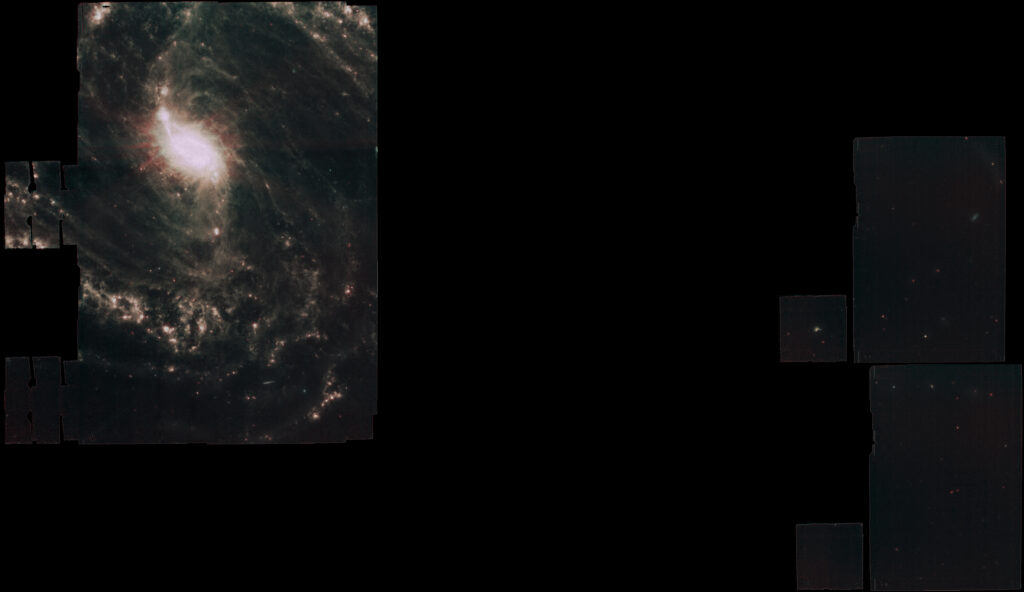
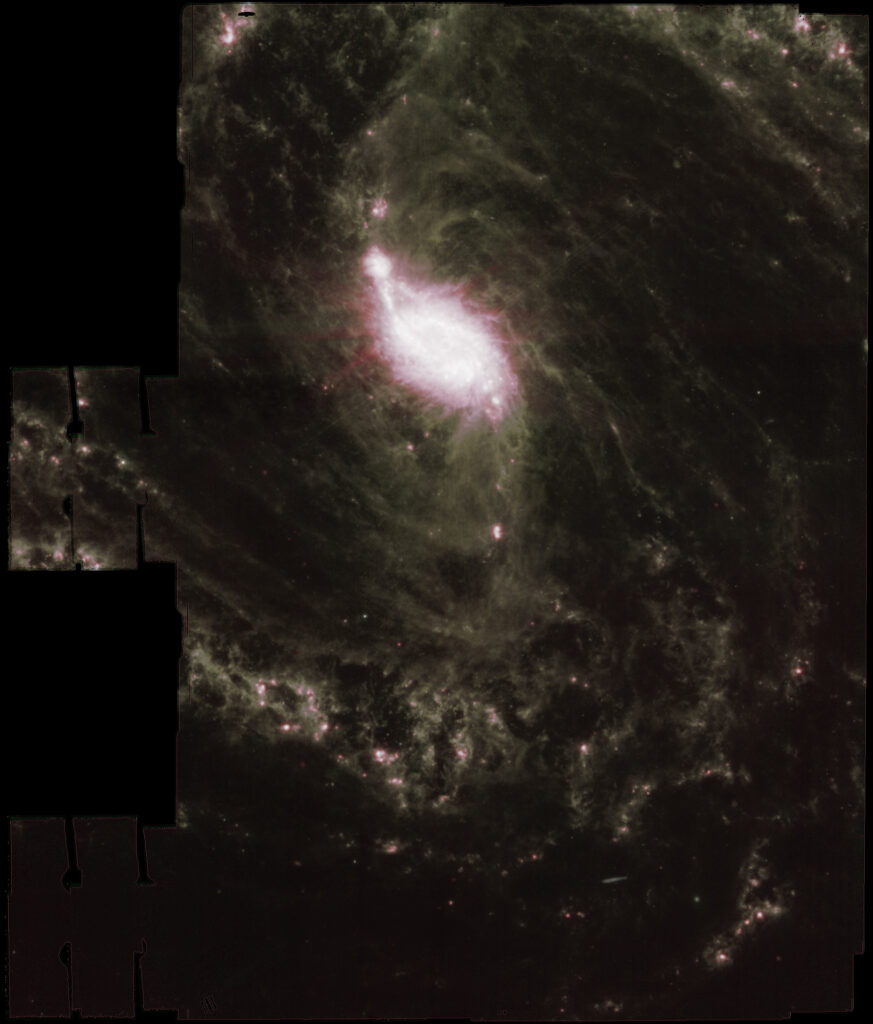
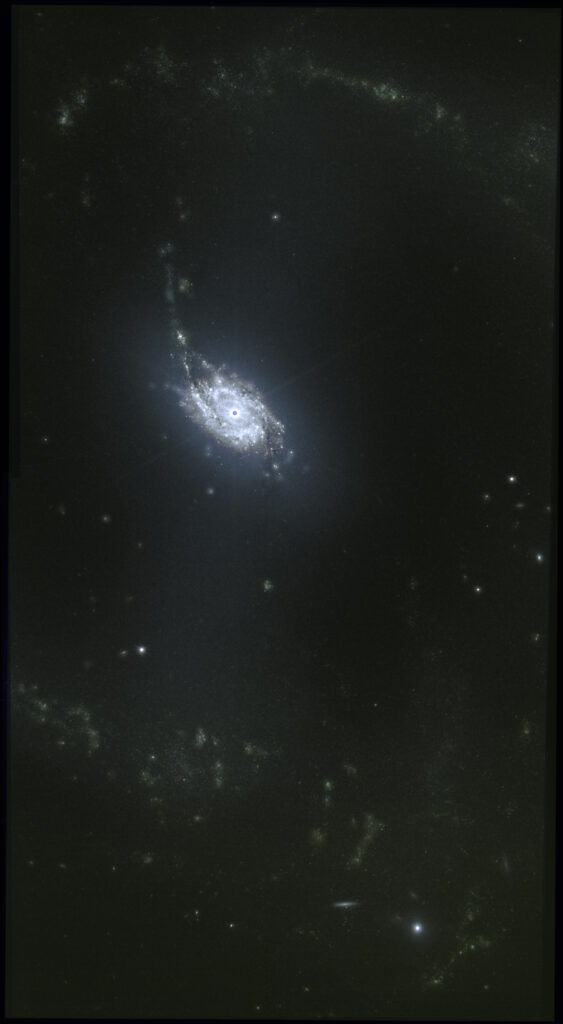
From Mikulksky Archive for Space Telescopes I downloaded raw calibrated .tif data focused about NGC 1365 Great Barred Spiral Galaxy, a double-barred spiral galaxy about 56 million light-years away in the constellation Fornax.
Among all data available I picked-up 3 sessions: a wide field MIRI mosaic by filters f770W, f1000W, f1130W and f2100W, a small field MIRI mosaic by the same filters f770W, f1000W, f1130W and f2100W a small NIRCAM field mosaic by filters f200W, f300M, f335M and f360M.