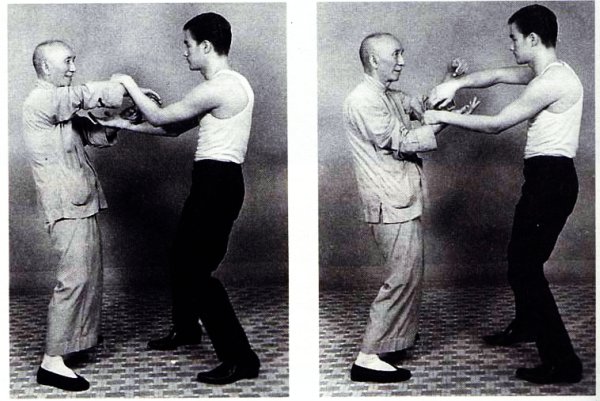
Regrets
As many readers will already know, Master Hawkins Cheung Hok Jin passed away on Sunday February 3rd 2019, in Los Angeles. Within the martial arts community regrets take many forms. One of my great regrets is that I had never had a chance to study with Hawkins Cheung. Yet he still had a profound effect on my understanding of both the nature of this art and the wider Wing Chun community. When Jon Nielson and I were researching our book on the development of Wing Chun, we frequently found ourselves coming back to the published accounts and interviews that Hawkins Cheung had provided over the years. We felt that these were some of the best, most reliable, descriptions of Wing Chun’s early years in Hong Kong (1950s-1960s) that one could hope to find.
Some of these accounts have already gained a fairly wide following within the Wing Chun community as they provided a remarkably frank assessment of Hawkins Cheung’s relationship with both Bruce Lee (his close friend and schoolmate), as well as Ip Man, his Sifu. It should be noted that throughout his life he spoke on many other subjects. He offered his own assessment of the true nature of Jeet Kun Do (JKD) and William Cheung’s innovations, styling his own instruction “classic Wing Chun” at least partially in response to these other developments within the community. Readers of Black Belt magazine will even remember Hawkins Cheung as an early and passionate advocate of a more combative approach to Taijiquan.
There is much that one could say about the life and career of such a remarkable martial artist. Cheung possessed a restless spirit always seeking progress. Throughout his life he sought to not just master Wing Chun, but to understand what made it work. This same curiosity would lead him to explore several other styles. Hawkins Cheung was a student of Goju-Ryu Karate in which he achieved a fourth Dan. He also developed a strong interest in Wu Taijiquan, which he approached with his signature direct practicality. After coming to the United States he set up a succession of successful schools in Los Angeles and introduced countless students (including individuals like Phillip Romero and Phil Morris) to Ip Man’s art.
By any standard Hawkins Cheung’s career was remarkable. He was one of just a handful of individuals who really shaped Wing Chun’s spread to North America. This brings us to a second, deeper, level of regret. Despite his many contributions, Cheung’s life and career are not well understood, except perhaps by his closest students. Bruce Lee was a luminary figure who ignited a Kung Fu fever. We would be remiss if we did not acknowledge his role in creating a global environment where Wing Chun might succeed. But we must also acknowledge his absolute talent for sucking the oxygen out of a room, or dominating any conversation that he might appear in.
Sadly, Hawkins Cheung is typically discussed only as Bruce’s sidekick. When reporters or researchers approached him, it was almost always to ask about his friend Bruce. This seemed to bother Cheung on a few levels, the most important of which was that Bruce had been a very close friend, and losing him was painful. Yet in death Lee’s myth grew to such proportions that it was impossible for anyone to escape his shadow.
All of this is in equal parts ironic and regrettable when thinking about Hawkins Cheung. It is ironic as he conveyed to current students so much historical knowledge about Hong Kong in the 1950s, yet accounts of his own career in the 1970s-1990s are extremely rare. It is regrettable as his life growing up in Hong Kong, and immigration to the West, mirrored Wing Chun’s global journey. Indeed, the two are inextricably linked. Serious historians and social scientists would better understand the process by which the Chinese martial arts succeeded as a global phenomenon if we could write his story. Even if Bruce Lee was critical to igniting the fire, it lasted because individuals like Hawkins Cheung were capable of feeding it.
Perhaps the first step toward better understanding is to simply appreciate what we already have. In the remainder of this post I will explore a basic outline of Hawkins Cheung’s life and contributions to the Asian martial arts. It is my hope that this will not only provide some insight into him, but also the ways in which history itself is memorialized and created. Indeed, traditional Chinese lineage structures have been making sense of the present by linking certain sorts of facts about the past for a long time. These highly stylized patterns of remembrance tell us something about the environment and sorts of challenges that our community faces. Yet other types of memory, ones that explicitly focus on the decades of quiet effort that are so often forgotten in our rush to construct martial immortality, are necessary to build a fuller understanding of how we got here and where we might be going. Hawkins Cheung’s life and career may be particularly important in this respect.
The Fighter
Only a limited amount of information about Hawkins Cheung’s early life seems to have made it into English language discussions. He was born sometime around 1940 and grew up in Kowloon. After 1949 the area became increasingly crowded with refugees and homeless individuals fleeing across the border with Communist controlled Guangdong. Even as a child Cheung was acutely aware of the bleak nature of life in Hong Kong emphasizing (as a repeated talking point in his later interviews) the problems with overcrowding, unemployment, homelessness and organized crime. These structural limitations would weigh heavily on the group of sometimes angry young men who gathered to train with Ip Man.
Still, Hawkins Cheung was more fortunate than most. He grew up in a relatively wealthy family. His father owned a luxurious car and could employ a professional driver to ferry his young son to school. It was also natural that Hawkins Cheung would be drawn to the martial arts given his small size, propensity for aggression and boundless energy. It was at the Francis Xavier Intermediate School that he first met and befriended the similarly predisposed Bruce Lee, who had recently been expelled (with good cause) from the much more prestigious LaSalle school. I will refer anyone who is interested in the gory details of that episode to Matthew Polly’s recent biography.
Being relatively affluent had other benefits as well. Hawkins Cheung reports that he was either 13 or 14 when he began to study Wing Chun kung fu with Ip Man, sometime around 1954. Interestingly, he was at first unaware when his friend Bruce also began to study with the same teacher, probably because the two were attending class at different times. Phil Morris suggests that later the two purposefully went to separate classes at least in part because the intensely competitive young men did not want to reveal their level of skill to a potential rival.
Some of our best accounts of life within Ip Man’s school come from a series of interviews that Hawkins Cheung gave to Inside Kung-Fu magazine in 1991. He speaks frankly about the competitive nature of outside challenge fights, but also the internal Chi Sao culture that developed among some of the younger Wing Chun students. Everyone wanted to be “top dog”, and Hawkins Cheung was at a real disadvantage due to his small size. I think that many Wing Chun students today will be able to relate to the frustrations that he expresses in these interviews.
Interestingly Ip Man, who didn’t typically handle the day to day training of the younger students, intervened at a point when he may have been considering quitting, guided him through an exploration of the basic defensive structures in the art’s unarmed forms. This helped Hawkins Cheung to build an understanding of Wing Chun that worked for him. Readers should remember that even by Hong Kong standards Ip Man was a pretty short individual of slight build. It would have been hard to think of a better mentor when addressing these problems.
Hawkins Cheung continued to study with Ip Man until 1959. One of the most important, yet often overlooked, causes of Wing Chun’s global success was the chronic under-development of Hong Kong’s educational sector in the 1950s and 1960s. There simply were not enough slots at Hong Kong University for all of the good students coming out the city’s school system. Nor were there enough high paying jobs to satisfy the children of the city’s middle class. The fact that Hong Kong was a British territory meant it was entirely possible for the children of wealthy families to do something about this.
Ip Ching has noted that many of his father’s better off young students traveled to North America, Australia or Europe to pursue both University degrees and better job prospects. Bruce Lee was far from alone in this exodus. Indeed, this pattern of global dispersal ensured that when Wing Chun became famous there were already a handful of well qualified individuals spread throughout the globe who could promote the art. Meanwhile, others had already acquired the language skills and life experience necessary to immigrate to the West and set up schools of their own.
Hawkins Cheung decided to further his educational prospects in Australia, but it seems that many of his experiences there were far from positive. As he noted in subsequent interviews, WWII had resulted in a high degree of anti-Japanese/anti-Asian prejudice, and it was not uncommon for Chinese students to be subject to racist attacks and other forms of violence. There were also tensions within the local Asian expatriate community, and Hawkins Cheung reports frequent fights with Thai kickboxers.
After finishing college Cheung returned to Hong Kong in 1962. He continued to study with Ip Man (now as a more senior student) until the time of his death in 1972. Adding things up, it appears that Hawkins Cheung enjoyed about 15 years of study as Ip Man’s student, both before and after college. While many individuals trained with Ip Man, due to retention problems and Ip Man’s many moves, relatively few students could claim such long periods of continuous training.
While in Hong Kong, Hawkins Cheung explored other arts, including Goju-Ryu Karate. Despite what one might assume, it was not uncommon for Chinese individuals to study Japanese arts (in either Hong Kong or Australia) during this period. What was much less common was for someone to maintain close ties to both communities while gaining a high degree of expertise. These styles were, after all, peer competitors.
Cheung relates that he was fascinated by the speed and power that Goju-Ryu practitioners could project through years of practice. He desperately wanted to learn how to counter this using Wing Chun structures, as well as to improve his own abilities. Yet he was also attracted to Karate as it offered a place where legal, socially approved, sparring could happen without the fear of police or gang involvement. He considered this essential to his training.
In fact, it seems that Hawkins Cheung was almost as skilled a diplomat as he was fighter. That might be a surprise given his often direct, kinetic and demanding teaching ethos. But even within the complex and fractured political landscape that emerged following Ip Man’s death, it is hard to think of any of his students who immigrated to the West who were more generally liked. As anyone who has read his articles or interviews knows, Hawkins Cheung was not shy about making his opinions known. Whether the subject was the true nature of JKD or the Taijiquan’s combative potential, Cheung was always willing to wade into the fray. Yet he remained almost universally respected. As any political scientist can tell you, diplomacy is also a martial art.
Hawkins Cheung immigrated to the United States in the late 1970s, a few years after Ip Man’s death. I have not been able to figure out much about his first few critical years. Yet by 1980 he was running a school with Dan Inosanto in Culver City Los Angeles. In a two-part article published in Wing Chun Illustrated in September 2017, Phillip Romero relates how he first discovered Cheung and began to train at his school.
Romero’s reminisces are valuable and readers are encouraged to head on over and examine them in full. They suggest an outline of the California period of Cheung’s career. But beyond that, they provide the same sorts of highly textured description of a school life that Hawkins Cheung himself had given us when describing his own training with Ip Man. Indeed, these rich descriptions are every bit as valuable to students of martial arts studies as any biographical details that may be related.
Romero paints a picture (largely supported by accounts from other students) of Hawkins Cheung as a demanding teacher. If as Sifu he embodied the “fatherly” archetype, his was the exacting and goal driven Chinese patriarch.
On a more technical level, as a still relatively young man he was concerned with how Wing Chun structures could be made to work in a variety of combative environments. The sorts of students who thrived in his early schools were those willing to risk bruises, split lips and other injuries in full contact drills and sparring that didn’t employ the sorts of safety equipment that would now be standard issue. Rather than MMA gloves (which did not yet exist) Romero relates how he found Cheung and his students using lightly padded gardening gloves where the fingers had been cut off.
Romero followed Cheung through multiple school locations. After closing his martial arts supply business (something that I would like to learn more about) to focus exclusively on teaching Hawkins Cheung opened a larger, two story school on Venice Blvd., “not far from the Culver mall.” This must have been a good location as Romero goes on to describe nightly classes with over 90 students split into three separate sections. This was followed up by another class for the senior students who helped to teach large sections of beginners. Still, not everyone was interested in the intensity and “reality” of the training on offer.
I must confess, however, that many of the reminisces of Cheung’s training in this period remind me of the sorts of contact levels and expectations that I experienced when I began my own Wing Chun apprenticeship some years later. Prior to the eruption of the UFC, MMA and BJJ there was more combative interest (and talent) being invested into the traditional striking arts. Yet every art has a certain reputation, or set of social expectations, which allows it to survive in a competitive marketplace. These seem to have changed dramatically for many systems following the rise of MMA.
I have often wondered whether the perceived combat deficiency of Wing Chun really reflects fundamental shortcomings in the system, or if a more sociological explanation is needed. By in large, the sorts of students who are willing to sacrifice the most and train the hardest are now siphoned directly into an entirely different set of social discourses around the modern combat sports. My friend Sixt Wetzler attempted to provide a theoretical basis for this sort of observation in an article that he wrote on applying systems theory to explain change within the martial arts communities. Still, a fuller and more granular exploration of what was going on in within Hawkins Cheung’s large Wing Chun community in the 1980s and 1990s might prove an interesting test case for these sorts of models.
In 1989 Hawkins Cheung closed the Ventura Blvd. school, and opened his final location a few miles away. This third school ran until 2014. It seems that with age his interests and teaching methods evolved (though his intensity did not necessarily mellow). And Romero points out that the blossoming of BJJ and MMA had a definite impact on the type of training that happened.
Still, Cheung’s contributions to the global martial arts community were not confined to his teaching activities. His name appeared in martial arts magazines, both in articles and letters, throughout the 1980s. Nor did he confine his contributions to the discussion of Wing Chun. He even emerged a popular advocate of a more combative understanding of Taijiquan, another art that he was deeply invested in.
In the early 1990s Hawkins Cheung gave what can only be considered a seminal (four-part) interview to Inside Kung Fu magazine. It must be considered mandatory reading by anyone interested in the development of Wing Chun during the post-WWII period. And it is hard to understate how much these articles shaped subsequent discussion of Bruce Lee’s legacy. Just check the footnotes of any of his biographical treatment published after 1992 to see what I mean.
Cheung was also something of an early adopter in the area of film and video recording. Steven Moody has noted that he collected 16 mm film of many of the most important figures in Wing Chun’s modern development. He is also reputed to have had films of various roof top challenge matches recorded earlier in Hong Kong. In an effort (only partially successful) to distribute some of this information, Hawkins Cheung established a Youtube Channel in 2013. There readers can find a manageable selection of his demonstration, discussions and interviews. He even posted some of his engagement with Wu and Chen style Taijiquan. In fact, you probably owe it to yourself to check out this vintage interview.
Memory
Memory is not an automatic thing, at either the individuals or the social level. We are all constantly curating our past as we choose what to remember and what we will allow to slip away. This process of remembering and forgetting is actually key to the construction of intergenerational Chinese martial arts communities. The social identity of a practitioner is defined, at least to some extent, by the lineage that they identify with.
Yet lineage is not history. It tells us a strong story about who we are now, but the ahistorical nature of the legend building process suggests that this way of viewing the martial arts is much less helpful if our goal is to understand how exactly we got here, or where we might be going.
The irony of Master Cheung’s life is that through his interviews he did much to preserve our history. Yet his story, like that of so many instructors in his generation, remains to be fully explored. Even in death he is still remembered as “Bruce Lee’s friend,” which is true, and something that he was proud of. Yet if this is the only fact that we remember, we are in danger of forgetting so much more about how Wing Chun evolved as it moved onto the global stage.
It is my fervent hope that in the coming months we will see more detailed remembrances and discussions of a critical career, one that should not be forgotten. But we should also take this moment to ask what other work must be done. Oral history projects are an important means by which non-specialists can contribute to the preservation of martial arts communities. It is something of a truism to say that the martial arts are always evolving, but we are in a particularly critical moment when so much of the post-WWII history of the TCMA will either be preserved or lost. All of this will only become our history if we first choose to remember it.
oOo
If you enjoyed this post you might also want to read: Remembering Chu Shong Tin and the Relationship between Theory and Observation in Chinese Martial Studies
oOo